Imagine stepping out into your own backyard and plucking fresh herbs, crisp vegetables, and juicy fruits to incorporate into your everyday meals. With a well-planned seasonal garden, you can enjoy the benefits of year-round healthy recipes right at your fingertips. In this article, we will explore simple and practical tips on how to plan and maintain a garden that provides a continuous supply of fresh and nutritious ingredients throughout the seasons. Whether you are a seasoned green thumb or a novice gardener, this guide will help you create a thriving garden, bringing you closer to a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle.
Choosing the Right Location for Your Garden
When it comes to starting your own garden, choosing the right location is crucial for the success of your plants. One important factor to consider is sunlight exposure. Most vegetables and herbs thrive in full sun, which means they need at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. Before deciding on a spot for your garden, observe how the sun moves across your yard throughout the day. This will help you determine which areas receive the most sunlight and which are more shaded.
Another key factor to consider is the soil quality. Plants rely on soil for their nutrients, so it’s essential to assess the soil in your potential garden location. Take a look at the soil’s texture, composition, and fertility. Sandy soil drains quickly but may require more frequent watering, while clay soil retains moisture but can be heavy and compact. The ideal soil for most plants is loamy soil, which is a balanced combination of sand, silt, and clay. Consider conducting a soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient content, as this information can help you amend the soil appropriately.
Lastly, determine the space availability in your yard. Consider the size of your garden and how much space you need for each plant. Some vegetables, like tomatoes or zucchini, require more room to spread out, while others, like herbs or lettuce, can be grown in tighter spaces. Take into account any existing structures or trees that may obstruct sunlight or limit the available space. Your garden should be easily accessible for maintenance and harvesting, so keep that in mind when selecting the location.
Determining the Garden Size
Before diving into the fun part of choosing plant varieties, take some time to determine the size of your garden. This will depend on a few factors, including your kitchen needs, available time and resources, and the number of people you aim to feed.
First, consider your kitchen needs. Are you an avid cook who uses fresh herbs and vegetables frequently? Do you enjoy canning or preserving your harvest for future use? By assessing your culinary habits, you can estimate the volume and variety of produce you’ll need throughout the year.
Next, evaluate the available time and resources you can dedicate to your garden. If you have limited time or physical capabilities, it’s best to start with a smaller garden that’s easier to maintain. On the other hand, if you have more time and resources, you can expand your garden and experiment with a wider variety of plants.
Lastly, consider the number of people you want to feed with your garden. If you have a large family or plan to share your produce with friends or neighbors, you’ll need a larger garden to meet the demand. Alternatively, if you’re only growing for yourself or a small household, a smaller garden may be sufficient.

Deciding on the Plant Varieties
Now that you have determined the size of your garden, it’s time to choose the plant varieties that will thrive in your region. Start by researching suitable plants for your specific climate and growing conditions. Consider the average temperatures, frost dates, and rainfall patterns in your area. This information will help you select plants that are well-suited to your region and have a higher chance of success.
While considering the climate is important, don’t forget to also take into account your family’s preferences. Think about the vegetables and herbs you enjoy eating the most. Do you have any favorite recipes that feature specific ingredients? By selecting plants that your family loves, you’ll be more motivated to care for them and enjoy the bountiful harvest.
Additionally, take the opportunity to explore different types of vegetables and herbs. Don’t limit yourself to the familiar and popular choices. Try experimenting with unique or heirloom varieties to add diversity to your garden. You never know, you might discover a new favorite vegetable or herb.
Planning the Seasonal Rotation
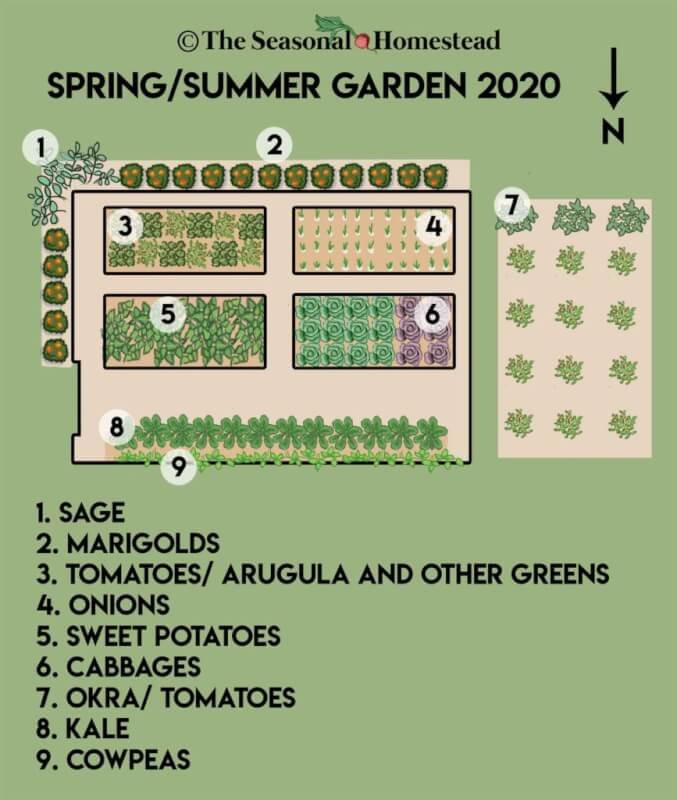
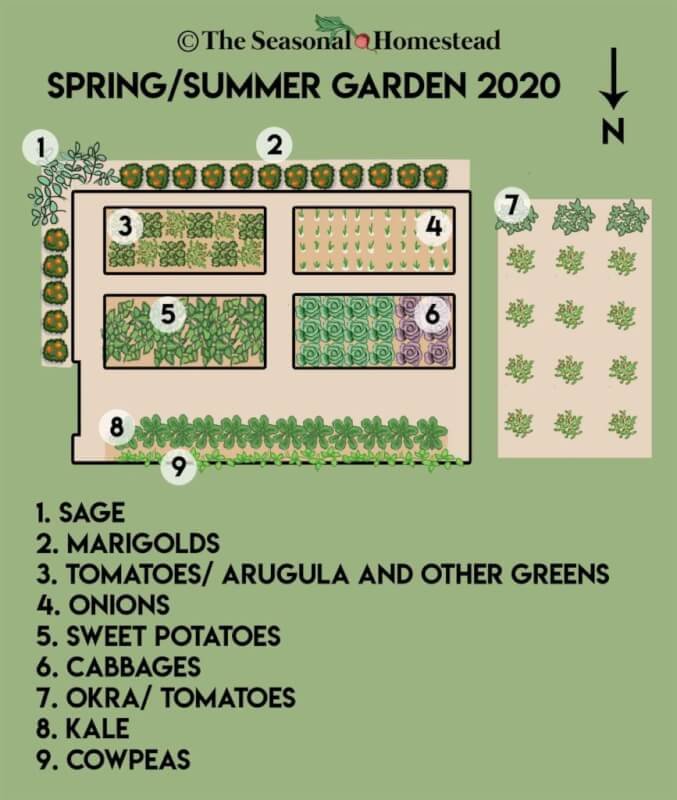
To ensure the long-term health and productivity of your garden, it’s crucial to plan for seasonal crop rotation. Crop rotation involves changing the location of crops within your garden each year to prevent the buildup of pests, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies. By following crop rotation principles, you can protect the overall health of your garden and improve yields.
Start by dividing your garden into sections based on the types of crops you plan to grow. For example, one section can be dedicated to leafy greens, another to root vegetables, and a third to legumes or fruiting plants. Each year, rotate these sections to new spots within your garden to disrupt any pests or diseases that might have overwintered in the soil.
Creating a planting schedule will also help you manage crop rotation effectively. Plan ahead and consider the recommended planting dates for each crop. Some plants thrive in the cooler months, while others prefer the warmth of summer. By strategically planting your crops based on their preferred seasons, you can maximize their growth and yield potential.

Preparing the Soil
A healthy garden starts with healthy soil. Before planting your seeds or seedlings, it’s important to prepare the soil properly. Three key steps in soil preparation include testing the pH level, amending the soil with organic matter, and adding essential nutrients.
Testing the pH level of your soil will determine its acidity or alkalinity, which affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Most vegetables prefer soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. You can test your soil using a pH testing kit or by sending a soil sample to a local agricultural extension office. If the pH level is too far from the optimal range, you can adjust it by adding soil amendments such as lime or sulfur.
The next step is to amend the soil with organic matter. Organic matter improves soil fertility, water retention, and structure. You can add materials such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold to enrich your soil. Spread a layer of organic matter over the top of your garden beds and gently incorporate it into the soil using a garden fork or tiller. This will help improve nutrient content and overall soil structure.
Lastly, ensure your soil has the essential nutrients necessary for plant growth. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are three primary nutrients that plants need in varying amounts. You can add balanced organic fertilizers or specific nutrient supplements to provide the necessary elements for your plants. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and apply it evenly over the soil before planting.
Starting Seeds Indoors
To extend your growing season and have a head start on your garden, consider starting seeds indoors. This allows you to control the growing conditions and ensure the success of your plants before transplanting them outside.
Start by collecting seed catalogs or researching reputable seed suppliers online. Look for varieties that are suited to your region and match your preferences. Choose high-quality seeds to give your plants the best chance of success.
Next, set up a seed-starting area in a well-lit space such as a windowsill or under grow lights. Fill seed trays or pots with seed-starting mix, a light and sterile medium that promotes seed germination. Sow the seeds according to the recommended depth and spacing for each variety. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, as excessive moisture can lead to damping-off disease.
Provide the right environmental conditions for your seedlings to thrive. Maintain a temperature range of 65 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 24 degrees Celsius) and ensure adequate airflow. Monitor the light levels and adjust the distance between the lights and the seedlings to prevent stretching or leggy growth.

Transplanting Seedlings
Once your seedlings have developed a strong root system and several sets of true leaves, they are ready to be transplanted into the garden. Proper preparation and care will help ensure a smooth transition for your young plants.
Prepare seedling pots or trays by filling them with a well-draining potting mix. Gently remove the seedlings from their original containers, being careful not to damage the roots. Dig a hole in the garden bed that is slightly larger than the root ball of the seedling. Place the seedling in the hole, making sure it is planted at the same depth as it was in the pot. Fill in the hole with soil, gently firming it around the seedling.
Before transplanting, it’s important to harden off the seedlings. This process involves gradually exposing them to the outdoor conditions to acclimate them to the change. Start by placing the seedlings in a sheltered, shaded area for a few hours each day. Gradually increase the exposure to sunlight and outdoor elements over the course of a week. This helps prevent transplant shock and allows the seedlings to adjust to the new environment.
Caring for Your Plants
To ensure the health and productivity of your plants, it’s important to provide proper care throughout the growing season. This includes watering and irrigation, weeding and mulching, as well as pruning and trellising.
Watering is crucial for plant growth, but it’s important to find the right balance. Most vegetables and herbs prefer consistent moisture, so aim for about one inch of water per week. Adjust watering based on rainfall and monitor the soil moisture levels. Water deeply and infrequently to encourage deep root growth. Use a soaker hose or drip irrigation system to deliver water directly to the root zone and minimize water loss through evaporation.
Weeding is a necessary task to prevent competition for nutrients and space. Regularly remove any weeds that sprout in your garden beds. Mulching can help suppress weed growth, conserve soil moisture, and regulate soil temperature. Apply a layer of organic mulch such as straw, wood chips, or leaves around your plants to reap these benefits.
Pruning and trellising are essential for plants that require support or shaping. Some vegetables, like tomatoes or cucumbers, benefit from being trained onto trellises or stakes to maximize space and airflow. Prune away any diseased or damaged foliage to prevent the spread of diseases and ensure healthy growth.

Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Every garden is prone to pests and diseases, but there are organic methods to manage and prevent these challenges. Start by identifying common garden pests in your area. Keep an eye out for signs of damage, such as chewed leaves, holes in fruits, or wilting foliage. Use organic pest control methods such as handpicking pests, applying natural sprays, or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or praying mantises.
Diseases can also affect your plants, causing wilting, discoloration, or stunted growth. Recognizing the symptoms of common plant diseases is crucial for prompt treatment. Organic treatments may include removing infected plants, improving air circulation, or using natural disease-fighting substances like copper sprays or neem oil. Remember to follow the instructions on any treatments you use and continuously monitor your plants for signs of improvement or further issues.
Adapting to Seasonal Changes
Gardens are constantly changing, and it’s important to adapt to the seasonal fluctuations to ensure the success of your plants. Prepare for temperature fluctuations by monitoring weather forecasts and protecting your plants from extreme heat or cold. Use shade cloth or row covers to provide shade during scorching summer days, and protect tender plants from frost with blankets or protective covers.
Sowing both cool-season and warm-season crops will help you maximize your garden’s productivity throughout the year. Cool-season crops like lettuce, spinach, or peas thrive in cooler temperatures and can be sown in early spring or late summer. Warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, or beans prefer warmer temperatures and should be sown after the danger of frost has passed.
Lastly, adjust your gardening practices to accommodate changes in sunlight exposure. As the seasons change, the angle and duration of sunlight will vary. Observe how the sunlight moves across your garden and make any necessary adjustments to maximize sunlight exposure for your plants. This will ensure they receive the necessary energy to grow and produce a bountiful harvest.
By following these guidelines and putting in the effort to plan and care for your garden, you’ll be rewarded with a thriving and productive oasis. The joy of harvesting fresh vegetables and herbs from your own backyard is unmatched, and the healthy recipes you can create using your homegrown produce will leave you feeling proud and satisfied. So get out there, get your hands dirty, and start planning your seasonal garden today!