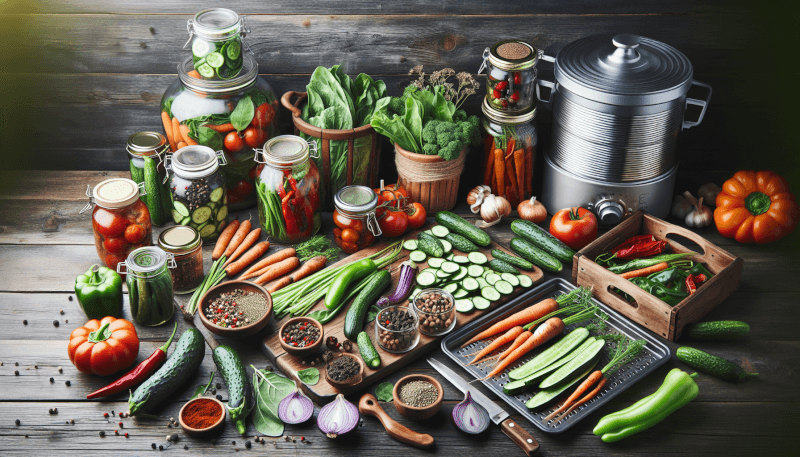
Preserving your garden vegetables for later use can be a rewarding and practical way to make the most of your bountiful harvest. Whether you have a surplus of tomatoes, cucumbers, or zucchinis, there are various techniques you can employ to ensure that your produce stays fresh and delicious throughout the year. From canning and freezing to dehydrating and pickling, this article will explore the best ways to preserve your garden vegetables and provide you with practical tips and tricks that will guarantee the longevity of your homegrown goodies. So, roll up your sleeves and get ready to discover the secrets of preserving nature’s bounty!
Canning
Canning is a wonderful method of preserving garden vegetables that allows you to savor their flavors even long after the harvest season is over. There are two popular canning methods – hot water bath canning and pressure canning.
Hot Water Bath Canning
Hot water bath canning is a simple and effective way to preserve high-acid foods such as tomatoes, pickles, and fruit preserves. The process involves placing jars of prepared food in a large pot of boiling water and allowing the heat to create a seal that keeps out harmful bacteria. This method is suitable for those who do not have a pressure canner and want to preserve their garden bounty safely.
Pressure Canning
Pressure canning is necessary for low-acid foods like beans, corn, and carrots. This method utilizes a pressure canner to achieve the high temperatures needed to safely preserve these items. The pressure canner creates a sealed chamber that allows the temperature to exceed the boiling point of water, effectively killing any bacteria or microorganisms that could cause spoilage. Pressure canning ensures that your vegetables stay fresh and preserve their taste and nutritional value for an extended period.
Freezing
Freezing is a convenient and quick method of preserving vegetables from your garden. It helps to retain the freshness and nutritional content of your produce while allowing you to enjoy them throughout the year.
Blanching
Blanching is an essential step before freezing vegetables. It involves briefly immersing the vegetables in boiling water and then plunging them into ice-cold water to stop the cooking process. Blanching helps to kill bacteria, enzymes, and microorganisms that may cause spoilage, while also preserving color, texture, and flavor.
Flash Freezing
Flash freezing is a great technique to ensure that your vegetables freeze individually and do not clump together. Lay the blanched vegetables on a baking sheet in a single layer and place it in the freezer. Once they are partially frozen, transfer them to freezer bags or airtight containers. This method prevents the vegetables from sticking together, making it easy for you to use only the amount you need.

Dehydrating
Dehydrating is an ancient preservation technique that involves removing the moisture from vegetables, thereby inhibiting the growth of bacteria and mold. There are different methods of dehydrating vegetables:
Air Drying
Air drying is a simple and traditional method of dehydrating vegetables. It involves slicing the vegetables into thin, uniform pieces and placing them in a single layer on a wire rack or mesh screen. Allow the vegetables to dry in a warm, well-ventilated area until they become crisp. Air drying works best for vegetables with lower water content, such as tomatoes, peppers, and herbs.
Oven Drying
Oven drying is a quick and efficient method of dehydrating vegetables. Preheat your oven to a low temperature (around 140°F) and place the sliced vegetables on a baking sheet. Leave the oven door slightly open to allow moisture to escape. Check on the vegetables regularly and remove them when they are dry and crisp.
Food Dehydrator
Investing in a food dehydrator is an excellent option for those who frequently preserve vegetables. Dehydrators have adjustable temperature settings and fans that circulate warm air, evenly drying the vegetables. Simply slice your vegetables, arrange them on the dehydrator trays, and set the temperature and time according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This method ensures thorough and consistent drying, resulting in great-tasting preserved vegetables.
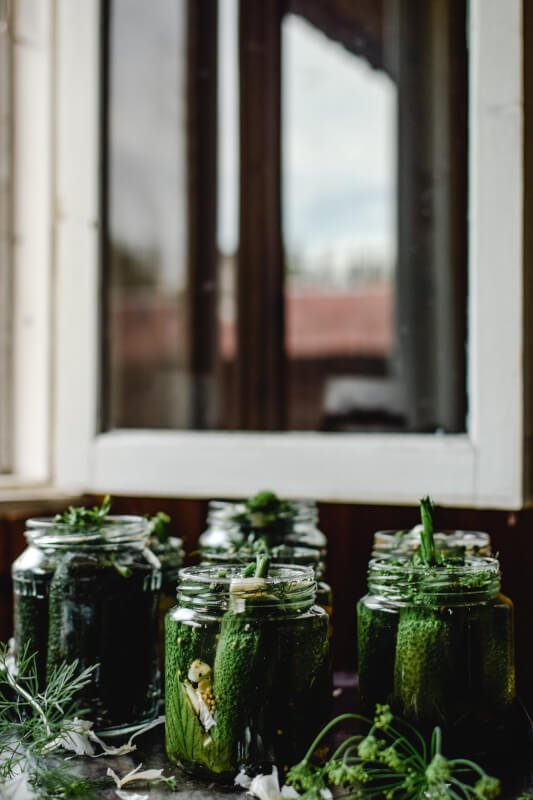
Pickling
Pickling is a versatile preservation method that involves immersing vegetables in a liquid solution, known as brine or vinegar, to create a tangy and flavorful product that can be enjoyed on its own or as a condiment.
Brined Pickles
Brined pickles are made by submerging vegetables in a saltwater solution. The brine enhances the flavor of the vegetables and prevents the growth of harmful bacteria. You can experiment with different spices and herbs to customize the flavor profile of your pickles. Once the vegetables have absorbed the brine and developed their desired taste, store them in sterilized jars in the refrigerator for long-lasting enjoyment.
Vinegar Pickles
Vinegar pickles involve covering vegetables with a solution of vinegar, water, and spices. The acidity of the vinegar acts as a natural preservative, keeping the vegetables safe from spoilage. Vinegar pickles can be made with cucumbers, onions, carrots, and other garden vegetables. These pickles can be stored in the refrigerator or processed using a hot water bath canning method for long-term shelf stability.

Fermenting
Fermenting vegetables is an ancient preservation technique that not only extends their shelf life but also enhances their flavor and nutritional value. Fermentation involves the natural breakdown of sugars by bacteria, resulting in the production of lactic acid, carbon dioxide, and other compounds.
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is a classic fermented cabbage dish that originates from Germany. To make sauerkraut, finely shred or chop cabbage and mix it with salt. Massage the salt into the cabbage until it begins to release its juices. Pack the cabbage tightly into sterilized jars, ensuring that all the cabbage is submerged in its own liquid. Allow the jars to ferment at room temperature for several days or weeks, depending on your desired flavor. Sauerkraut can be enjoyed as a side dish or added to sandwiches and salads.
Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean side dish made from fermented vegetables, primarily cabbage. It is packed with a complex blend of flavors and is known for its spicy kick. To make kimchi, prepare the vegetables by chopping them and salting them for a short period. Rinse the vegetables and mix them with a flavorful paste made from chili pepper flakes, garlic, ginger, and other spices. Pack the mixture tightly into jars and allow it to ferment at room temperature for a few days before transferring it to the refrigerator. Kimchi can be enjoyed on its own, as a side dish, or incorporated into various recipes.
Salting
Salting is a preservation method that involves using salt to draw out moisture from vegetables, creating an environment that inhibits the growth of bacteria and molds.
Dry Salting
Dry salting is a simple and effective way to preserve vegetables like cucumbers, eggplant, and zucchini. To dry salt, slice or chop the vegetables and sprinkle them generously with salt. Let the vegetables sit for a while to allow the salt to extract the moisture. Rinse the vegetables to remove excess salt, pat them dry, and store them tightly sealed in the refrigerator. Dry salted vegetables can be used in a variety of dishes, such as sandwiches, stir-fries, and salads.
Salt Brine
Salt brining is another method of preserving vegetables by immersing them in a saltwater solution. Create a brine by dissolving salt in water and submerge the vegetables. The salt brine helps maintain the texture and flavor of the vegetables while preserving them. Store the brined vegetables in sterilized jars in the refrigerator for an extended shelf life.

Cold Storage
Cold storage is an excellent preservation method for storing garden vegetables that do not require processing or additional preparation.
Root Cellaring
Root cellaring involves storing vegetables in a cool, dark, and humid space to extend their freshness and shelf life. Ideal vegetables for root cellaring include carrots, potatoes, beets, and turnips. Find a cool corner of your basement or a designated root cellar if available. Ensure proper ventilation and monitor the humidity levels to prevent rotting. Place the vegetables in bins or boxes with damp sand, sawdust, or straw to maintain their moisture. Regularly inspect the stored vegetables and remove any that are showing signs of spoilage.
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is a convenient way to preserve garden vegetables for short-term storage. Most vegetables benefit from being stored in a refrigerator crisper drawer or sealed plastic bags to maintain their freshness. However, it’s important to note that some vegetables, such as tomatoes and onions, should be stored at room temperature to prevent flavor and texture changes. Always check the specific storage requirements for each vegetable to ensure maximum quality and shelf life.
Vacuum Sealing
Vacuum sealing is a method of preserving garden vegetables that removes air from the packaging, creating a seal that helps prevent spoilage and freezer burn. This technique is particularly useful for freezing vegetables.
To vacuum seal your vegetables, ensure they are clean and dry before placing them in vacuum-sealable bags or containers. Use a vacuum sealer machine to remove the air from the packaging, creating an airtight seal. Properly sealed bags can be stored in the freezer, allowing your vegetables to stay fresh and retain their flavor for an extended period.
Preserving in Oil
Preserving vegetables in oil not only enhances their flavor but also helps preserve them for a longer period. This preservation method works well for vegetables such as sun-dried tomatoes, roasted peppers, and marinated artichokes.
To preserve vegetables in oil, ensure the vegetables are thoroughly cleaned and dried before placing them in sterilized jars or containers. Pack the vegetables tightly, leaving some headspace, and cover them completely with your preferred oil, such as olive oil. The oil acts as a barrier, preventing air and bacteria from reaching the vegetables. Store the jars in the refrigerator or a cool, dark pantry for safe preservation.
Herb and Spice Infusion
Infusing herbs and spices into vinegar or oil is a delightful way to preserve the flavors of your garden herbs and enhance a variety of dishes.
To create herb and spice infusions, gather your desired fresh herbs and spices, such as rosemary, thyme, peppercorns, or garlic cloves. Place the herbs and spices in sterilized jars or bottles and pour vinegar or oil over them, completely covering the ingredients. Seal the jars or bottles tightly and store them in a cool, dark place for a few weeks to allow the flavors to develop. The infused vinegar or oil can be used in salads, marinades, dressings, and various culinary creations.
Preserving garden vegetables allows you to enjoy the abundance of the harvest season year-round. Whether you choose canning, freezing, dehydrating, pickling, fermenting, salting, cold storage, vacuum sealing, preserving in oil, or herb and spice infusion, each method offers its unique benefits and flavors. With a little time and effort, you can savor the taste of your homegrown vegetables and create delicious meals throughout the year. Happy preserving!



